Navigator Audit Server Management
The Navigator Audit Server tracks and coalesces events from Cloudera Manager and stores them in the Navigator Audit database. This section provides a high level view of the auditing architecture and shows administrators how to use Cloudera Manager Admin Console to add the Navigator Audit Server to an existing cluster, how to configure some of its features.
Navigator Auditing Architecture
The figure below shows a high level view of the Cloudera Navigator auditing architecture:
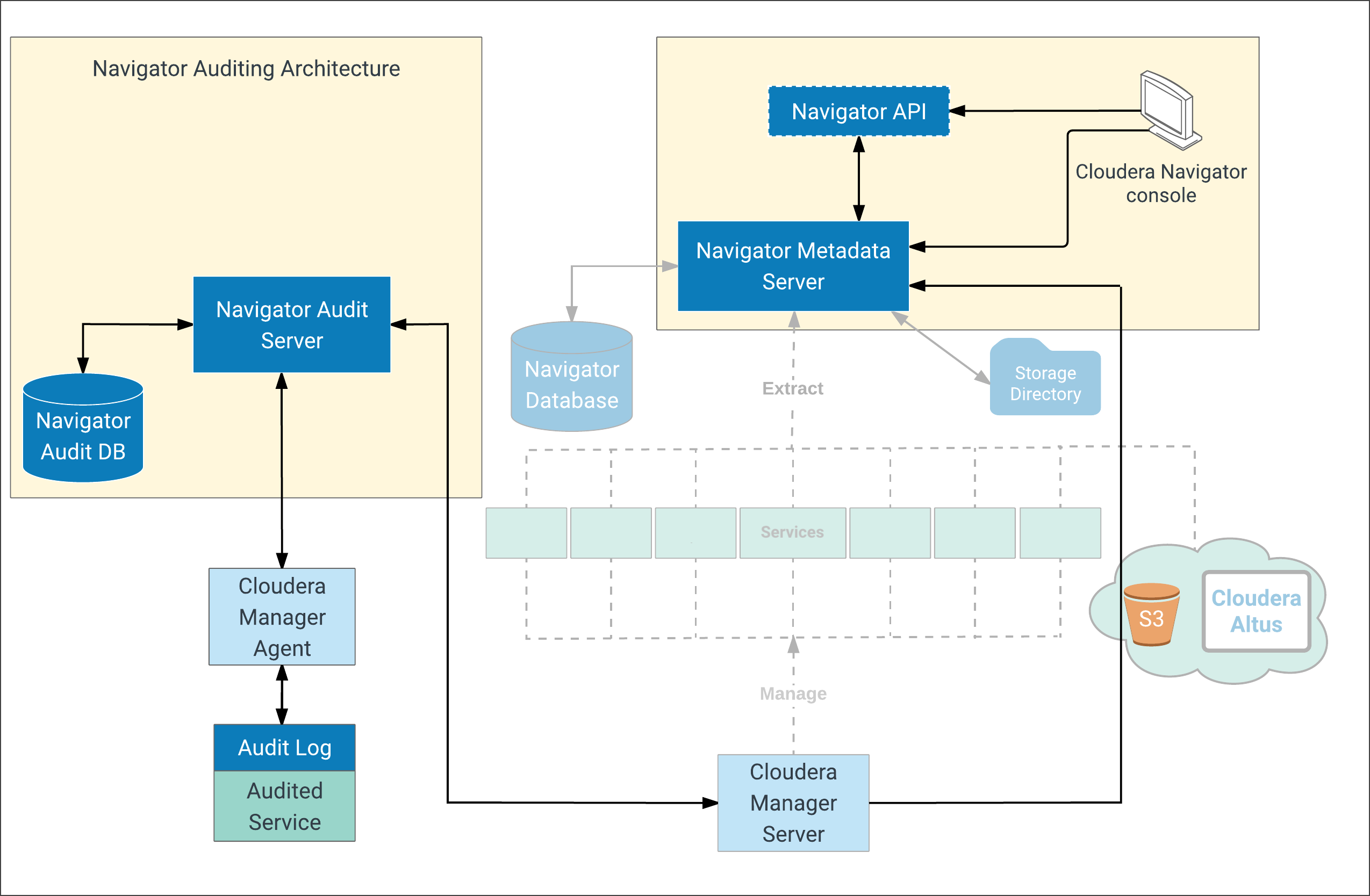
During system setup, plug-ins for the various services—HDFS, HBase, and Hive (HiveServer2, Beeswax servers) services, for example—are enabled. These plug-ins work with the service to collect and filter events emitted by the respective service, writing the events to an audit log on the local filesystem. Impala, Sentry, and the Cloudera Navigator Metadata Server also collect and filter events and write them to their respective audit log files.
 Note: When upgrading Cloudera Navigator, always check the requirements for any preliminary tasks or constraints due to service plug-ins.
Note: When upgrading Cloudera Navigator, always check the requirements for any preliminary tasks or constraints due to service plug-ins.Auditing Architecture In More Detail: How It Works
Here is some more detail about the auditing architecture and interaction among Cloudera Manager Agent, local log file, and Navigator Audit Server.
The Cloudera Manager Agent process on each host in the cluster:
- Monitors local audit log files
- Sends events captured in the logs to the Navigator Audit Server
- Retries sending any event that fails to transmit successfully
- Keeps track of successfully transmitted events from the logfile (offset position in the file) to prevent re-sending any already processed events after a system failure and restart
- Deletes old audit logs after successful transmission to the Navigator Audit Server
After any event is written to the audit log file (and assuming space available on the filesystem), its delivery is guaranteed. In other words, transient (in-memory) buffer handling is not involved in this part of the process. Audit logs are rotated and the Cloudera Manager Agent follows the rotation of the log.
The plug-in for each of the various services effectively writes the events to the audit log file. A plug-in that fails to write an event to the audit log file can either drop the event or can shut down the process in which it is running depending on the configured queue policy.
- Tracks and coalesces events obtained from Cloudera Manager
- Stores events to the Navigator Audit database
| Audited Service | Note |
|---|---|
| HBase | hbase-MASTER, hbase-REGIONSERVER |
| HDFS | hdfs-NAMENODE |
| Hive | Hive Server 2 only (hive-HIVESERVER2). Command line beeline (not hive). |
| Hue | |
| Impala | impala-IMPALAD (Auditing data and lineage data both collected by Cloudera Manager Agent). |
| Navigator Metadata Server | |
| Sentry | |
| Solr |
Continue reading:
| << Preventing Concurrent Logins from the Same User | ©2016 Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved | Setting Up Navigator Audit Server >> |
| Terms and Conditions Privacy Policy |