Managing the Sentry Service
This topic describes basic Sentry terminology and the Sentry privilege model:
Terminology
- An object is an entity protected by Sentry's authorization rules. The objects supported in the current release are server, database, table, URI, collection, and config.
- A role is a collection of rules for accessing a given object.
- A privilege is granted to a role to govern access to an object. Sentry allows you to assign the SELECT privilege to columns (only
for Hive and Impala). Supported privileges are:
Table 1. Valid privilege types and the objects they apply to Privilege Object ALL SERVER, TABLE, DB, URI CREATE SERVER, DATABASE INSERT SERVER, DB, TABLE REFRESH (Impala only) SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE SELECT SERVER, DB, TABLE, COLUMN - A user is an entity that is permitted by the authentication subsystem to access the service. This entity can be a Kerberos principal, an LDAP userid, or an artifact of some other supported pluggable authentication system.
- A group connects the authentication system with the authorization system. It is a collection of one or more users who have been granted one or more authorization roles. Sentry allows a set of roles to be configured for a group.
- A configured group provider determines a user’s affiliation with a group. The current release supports HDFS-backed groups and locally configured groups.
Privilege Model
- Allows any user to execute show function, desc function, and show locks.
- Allows the user to see only those tables, databases, collections, and configurations for which the user has privileges.
- Requires a user to have the necessary privileges on the URI to execute HiveQL operations that specify a location. Examples of such operations include LOAD, IMPORT, and EXPORT.
- Sentry provides column-level access control for tables in Hive and Impala. You can assign the SELECT privilege on a subset of columns in a table.
- In Beeline, you can grant privileges on an object that doesn't exist. For example, you can grant role1 on table1 and then create table1.
 Important:
Important:
- When Sentry is enabled, you must use Beeline to execute Hive queries. Hive CLI is not supported with Sentry and must be disabled.
- When Sentry is enabled, a user with no privileges on a database will not be allowed to connect to HiveServer2. This is because the use <database> command is executed as part of the connection to HiveServer2, which is why the connection fails. See HIVE-4256.
For more information, see Authorization Privilege Model for Hive and Impala, Authorization Privilege Model for Solr, and Using Kafka with Sentry Authorization.
Granting Privileges
 Note: In the following example(s), server1 refers to an alias Sentry uses for the associated Hive service. It does not refer to any physical server. This alias can be modified using the hive.sentry.server property in hive-site.xml. If you are using Cloudera Manager, modify the Hive property, Server Name for Sentry Authorization, in
the category.
Note: In the following example(s), server1 refers to an alias Sentry uses for the associated Hive service. It does not refer to any physical server. This alias can be modified using the hive.sentry.server property in hive-site.xml. If you are using Cloudera Manager, modify the Hive property, Server Name for Sentry Authorization, in
the category.server=server1->db=sales->table=customer->action=Select
sales_read = server=server1->db=sales->table=customers->column=Id->action=selectEach object must be specified as a hierarchy of the containing objects, from server to table, followed by the privilege granted for that object. A role can contain multiple such rules, separated by commas. For example, a role might contain the Select privilege for the customer and items tables in the sales database, and the Insert privilege for the sales_insights table in the reports database. You would specify this as follows:
sales_reporting = \ server=server1->db=sales->table=customer->action=Select, \ server=server1->db=sales->table=items->action=Select, \ server=server1->db=reports->table=sales_insights->action=Insert
Granting Privileges on URIs
Grant permissions on URIs to create functions, alter the location of a table, explicitly set the location of a table, and to import and export from a table with that location. A user must have ALL permissions on the URI to perform the following actions:
- Export from a table to a location
- Import from a table to a location
- Insert into a table at an S3 location
- Alter a table to change the location of the table
- Create a function from a jar file (requires other administrative settings as well)
For example, if you create the following table with an S3 location:
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE mytesttable (firstname STRING, lastname STRING, address STRING, city STRING, state STRING) ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY ',' LOCATION 's3a://mybucket/';
To insert data into the table, you must have ALL on the URI 's3a://mybucket' to execute the following command:
INSERT INTO TABLE mytesttable VALUES ('bilbo', 'baggends', 'bagend', 'hobbiton', 'shire');The URI represents the HDFS path you specify as part of a GRANT statement. The URI in the statement can look like a UNIX path, but can also be prefixed with hdfs:// to clarify that it is a URI.
The following command is an example of a GRANT privilege on a URI:
GRANT ALL ON URI '/user/hive/warehouse/customers' TO ROLE t_rex
The only privilege you can grant on a URI is ALL. For details about the GRANT ALL ON URI statement, see GRANT <Privilege> ON URIs (HDFS and S3A).
- hdfs://host:port/directory_A/directory_B
- hdfs://host:port/directory_A/directory_B/directory_C
- hdfs://host:port/directory_A/directory_B/directory_C/directory_D
- hdfs://host:port/directory_A/directory_B/directory_E
URIs are not applied as HDFS ACLs. The How-To article and video, How to Verify that HDFS ACLs are Synching with Sentry , gives an example of a GRANT statement on a URI that does not affect an HDFS ACL change. For information on what does trigger an HDFS ACL change, see Prompting HDFS ACL Changes.
 Warning: Because the NameNode host and port are used when you grant privileges on a URI, it
is strongly recommended that you use HDFS High Availability (HA). This ensures that the URI will remain constant even if the NameNode changes.
Warning: Because the NameNode host and port are used when you grant privileges on a URI, it
is strongly recommended that you use HDFS High Availability (HA). This ensures that the URI will remain constant even if the NameNode changes.User to Group Mapping
Minimum Required Role: Configurator (also provided by Cluster Administrator, Full Administrator)
- Sentry - Groups are looked up on the host the Sentry Server runs on.
- Hive - Groups are looked up on the hosts running HiveServer2 and the Hive Metastore.
- Impala - Groups are looked up on the Catalog Server and on all of the Impala daemon hosts.
Group mappings in Sentry can be summarized as in the figure below.
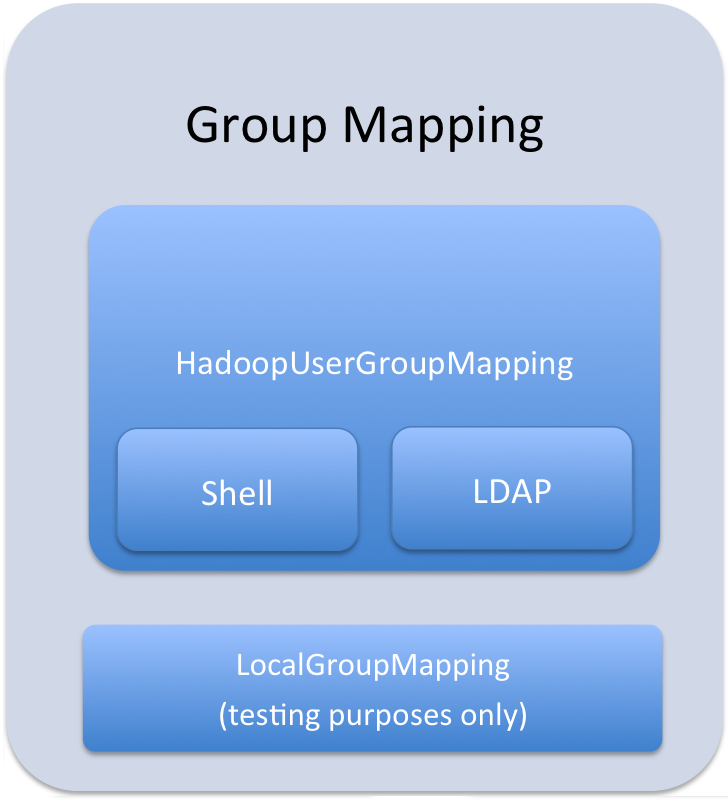
The Sentry service only uses HadoopUserGroup mappings. See Configuring LDAP Group Mappings for details on configuring LDAP group mappings in Hadoop.
Authorization Privilege Model for Hive and Impala
Privileges can be granted on different objects in the Hive warehouse. Any privilege that can be granted is associated with a level in the object hierarchy. If a privilege is granted on a container object in the hierarchy, the base object automatically inherits it. For instance, if a user has ALL privileges on the database scope, then (s)he has ALL privileges on all of the base objects contained within that scope.
 Important:
Important:
Note that because of this object hierarchy, it is possible for a user to read data from a database that the user does not have access to. For example, you have two roles:
- role1 - full access to database1 and database2
- role2 - full access to database1, no access to database2
A user with role1 can create a view in database1 based on a table in database2. Because role2 has access to database1, a user with role2 can read the data in that view from database2.
Object Hierarchy
Server
URI
Database
Table
Partition
Columns
View
| Privilege | Object |
|---|---|
| INSERT | DB, TABLE |
| SELECT | DB, TABLE, VIEW, COLUMN |
| ALL | SERVER, TABLE, DB, URI |
| Base Object | Granular privileges on object | Container object that contains the base object | Privileges on container object that implies privileges on the base object |
|---|---|---|---|
| DATABASE | ALL | SERVER | ALL |
| TABLE | INSERT | DATABASE | ALL |
| TABLE | SELECT | DATABASE | ALL |
| COLUMN | SELECT | DATABASE | ALL |
| VIEW | SELECT | DATABASE | ALL |
Privilege Tables for Hive and Impala
The following three tables list the privileges that are required to perform operations for Hive, Impala, and operations that apply to both Hive and Impala. All possible privileges are listed for each operation. For example, to perform the ALTER DATABASE command in Hive, the user can have the ALL privilege on the SERVER or the DATABASE.
| Operation | Required Privileges | Scope |
|---|---|---|
| ALTER DATABASE | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE |
| ALTER TABLE .. CLUSTERED BY.. SORTED BY | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| ALTER TABLE .. ENABLE / DISABLE | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| ALTER TABLE .. PARTITION ENABLE / DISABLE | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| ALTER TABLE .. PARTITION.. RENAME TO PARTITION | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| ALTER TABLE TOUCH | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| ALTER TABLE TOUCH PARTITION | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| ANALYZE TABLE | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| SELECT | TABLE | |
| INSERT | TABLE | |
| CREATE INDEX | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| CREATE | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE | |
| ANALYZE TABLE | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| SELECT | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE, COLUMN | |
| INSERT | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE | |
| REFRESH | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE | |
| DESCRIBE TABLE .. PARTITION | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| SELECT | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE | |
| INSERT | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE | |
| DROP INDEX | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| EXPORT TABLE | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| GRANT PRIVILEGE | Allowed only for Sentry admin users | |
| IMPORT TABLE | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE |
| INSERT OVERWRITE DIRECTORY | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| INSERT | TABLE | |
| MSCK REPAIR TABLE | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| REVOKE PRIVILEGE | Allowed only for Sentry admin users | |
| SHOW COLUMNS
The output for this operation filters columns that the user does not have explicit SELECT access to. |
ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| SELECT | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE | |
| INSERT | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE | |
| SHOW INDEXES | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| SELECT | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE | |
| INSERT | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE | |
| CREATE | SERVER | |
| SHOW TABLE PROPERTIES | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| SELECT | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE | |
| INSERT | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| Operation | Required Privileges | Scope |
|---|---|---|
| COMPUTE INCREMENTAL STATS | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| COMPUTE STATS | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| DESCRIBE TABLE | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| SELECT | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE, COLUMN | |
| INSERT | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE | |
| REFRESH | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE | |
| CREATE | SERVER, DATABASE | |
| EXPLAIN INSERT | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| INSERT | DATABASE, TABLE | |
| EXPLAIN SELECT | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| SELECT | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE, COLUMN | |
| INVALIDATE METADATA | ALL | SERVER |
| REFRESH | SERVER | |
| INVALIDATE METADATA <table name> | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| REFRESH | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE | |
| REFRESH <table name> or REFRESH <table name> PARTITION (<partition_spec>) | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| REFRESH | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE | |
| SHOW COLUMN STATS | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| SELECT | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE | |
| INSERT | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE | |
| REFRESH | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| Operation | Required Privileges | Scope |
|---|---|---|
| ALTER TABLE .. ADD COLUMNS | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| ALTER TABLE .. ADD PARTITION | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| ALTER TABLE .. ADD PARTITION or ALTER TABLE .. ADD PARTITION LOCATION | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| ALTER TABLE .. CHANGE COLUMN | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| ALTER TABLE .. DROP COLUMN | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| ALTER TABLE .. DROP PARTITION | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| ALTER TABLE .. SET FILEFORMAT | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| ALTER TABLE .. PARTITION SET SERDEPROPERTIES | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| ALTER TABLE .. RENAME | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE |
| ALTER TABLE .. REPLACE COLUMNS | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| ALTER TABLE .. SET FILE FORMAT | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| ALTER TABLE .. SET LOCATION | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| ALTER TABLE .. SET SERDEPROPERTIES | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| ALTER TABLE .. SET TBLPROPERTIES | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| ALTER VIEW
This operation is allowed if you have column-level SELECT access to the columns being used. |
ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, VIEW |
| ALTER VIEW .. RENAME | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, VIEW |
| CREATE DATABASE | ALL | SERVER |
| CREATE | SERVER | |
| CREATE FUNCTION | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE |
| CREATE | SERVER, DATABASE | |
| CREATE TABLE | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE |
| CREATE | SERVER, DATABASE | |
| CREATE TABLE .. AS SELECT
This operation is allowed if you have column-level SELECT access to the columns being used. |
ALL | SERVER, DATABASE |
| CREATE VIEW
This operation is allowed if you have column-level SELECT access to the columns being used. |
ALL | SERVER, DATABASE |
| DESCRIBE DATABASE | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE |
| SELECT | SERVER, DATABASE | |
| INSERT | SERVER, DATABASE | |
| REFRESH | SERVER, DATABASE | |
| DROP DATABASE | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE |
| DROP FUNCTION | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE |
| DROP TABLE | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE,TABLE |
| DROP VIEW | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, VIEW |
| INSERT | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| INSERT | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE | |
| INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| INSERT | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE | |
| LOAD DATA | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| INSERT | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE | |
| SELECT | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| SELECT | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE, COLUMN | |
| SELECT COLUMN | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| SELECT | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE, COLUMN | |
| SELECT TABLE | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| SELECT | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE | |
| SELECT TABLE .. JOIN | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| SELECT | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE | |
| SELECT VIEW
You can grant the SELECT VIEW privilege on a view to give users access to specific columns of a table that they do not otherwise have access to. |
ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, VIEW |
| SELECT | SERVER, DATABASE, VIEW | |
| SHOW CREATE TABLE | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| SELECT | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE | |
| INSERT | DATABASE, TABLE | |
| REFRESH | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE | |
| SHOW GRANT ROLE | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| SELECT | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE | |
| INSERT | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE | |
| SHOW PARTITIONS | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| SELECT | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE | |
| INSERT | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE | |
| REFRESH | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE | |
| SHOW TABLES
The output includes all the tables the user has table-level or column-level access to. |
ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| SELECT | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE, COLUMN, VIEW | |
| INSERT | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE | |
| CREATE | SERVER, DATABASE | |
| REFRESH | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE | |
| USE | ALL | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
| SELECT | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE, COLUMN, VIEW | |
| INSERT | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE | |
| CREATE | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE | |
| REFRESH | SERVER, DATABASE, TABLE |
Authorization Privilege Model for Solr
The tables below refer to the request handlers defined in the generated solrconfig.xml.secure. If you are not using this configuration file, the below may not apply.
admin is a special collection in Sentry used to represent administrative actions. A non-administrative request may only require privileges on the collection or config on which the request is being performed. This is called either collection1 or config1 in these tables. An administrative request may require privileges on both the admin collection and collection1. This is denoted as admin, collection1 in the tables below.
 Note: If no privileges
are granted, no access is possible. For example, accessing the Solr Admin UI requires the QUERY privilege. If no users are granted the QUERY privilege, no access to the Solr Admin UI is possible.
Note: If no privileges
are granted, no access is possible. For example, accessing the Solr Admin UI requires the QUERY privilege. If no users are granted the QUERY privilege, no access to the Solr Admin UI is possible.| Request Handler | Required Collection Privilege | Collections that Require Privilege |
|---|---|---|
| select | QUERY | collection1 |
| query | QUERY | collection1 |
| get | QUERY | collection1 |
| browse | QUERY | collection1 |
| tvrh | QUERY | collection1 |
| clustering | QUERY | collection1 |
| terms | QUERY | collection1 |
| elevate | QUERY | collection1 |
| analysis/field | QUERY | collection1 |
| analysis/document | QUERY | collection1 |
| update | UPDATE | collection1 |
| update/json | UPDATE | collection1 |
| update/csv | UPDATE | collection1 |
| Collection Action | Required Collection Privilege | Collections that Require Privilege |
|---|---|---|
| create | UPDATE | admin, collection1 |
| delete | UPDATE | admin, collection1 |
| reload | UPDATE | admin, collection1 |
| createAlias | UPDATE | admin, collection1
 Note: collection1 here refers to the name of the alias, not the
underlying collection(s). For example, http://YOUR-HOST:8983/ solr/admin/collections?action= CREATEALIAS&name=collection1
&collections=underlyingCollection Note: collection1 here refers to the name of the alias, not the
underlying collection(s). For example, http://YOUR-HOST:8983/ solr/admin/collections?action= CREATEALIAS&name=collection1
&collections=underlyingCollection |
| deleteAlias | UPDATE | admin, collection1
 Note: collection1 here refers to the name of the alias, not the
underlying collection(s). For example, http://YOUR-HOST:8983/ solr/admin/collections?action= DELETEALIAS&name=collection1 Note: collection1 here refers to the name of the alias, not the
underlying collection(s). For example, http://YOUR-HOST:8983/ solr/admin/collections?action= DELETEALIAS&name=collection1 |
| syncShard | UPDATE | admin, collection1 |
| splitShard | UPDATE | admin, collection1 |
| deleteShard | UPDATE | admin, collection1 |
| Collection Action | Required Collection Privilege | Collections that Require Privilege |
|---|---|---|
| create | UPDATE | admin, collection1 |
| rename | UPDATE | admin, collection1 |
| load | UPDATE | admin, collection1 |
| unload | UPDATE | admin, collection1 |
| status | UPDATE | admin, collection1 |
| persist | UPDATE | admin |
| reload | UPDATE | admin, collection1 |
| swap | UPDATE | admin, collection1 |
| mergeIndexes | UPDATE | admin, collection1 |
| split | UPDATE | admin, collection1 |
| prepRecover | UPDATE | admin, collection1 |
| requestRecover | UPDATE | admin, collection1 |
| requestSyncShard | UPDATE | admin, collection1 |
| requestApplyUpdates | UPDATE | admin, collection1 |
| Request Handler | Required Collection Privilege | Collections that Require Privilege |
|---|---|---|
| LukeRequestHandler | QUERY | admin |
| SystemInfoHandler | QUERY | admin |
| SolrInfoMBeanHandler | QUERY | admin |
| PluginInfoHandler | QUERY | admin |
| ThreadDumpHandler | QUERY | admin |
| PropertiesRequestHandler | QUERY | admin |
| LoginHandler | QUERY, UPDATE (or *) | admin |
| ShowFileRequestHandler | QUERY | admin |
| Config Action | Required Collection Privilege | Collections that Require Privilege | Required Config Privilege | Configs that Require Privilege |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CREATE | UPDATE | admin | * | config1 |
| DELETE | UPDATE | admin | * | config1 |
| << Configuring Sentry Authorization for Cloudera Search | ©2016 Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved | Synchronizing HDFS ACLs and Sentry Permissions >> |
| Terms and Conditions Privacy Policy |