Introduction to Cloudera Manager Deployment Architecture
Cloudera Manager consists of the following software components:
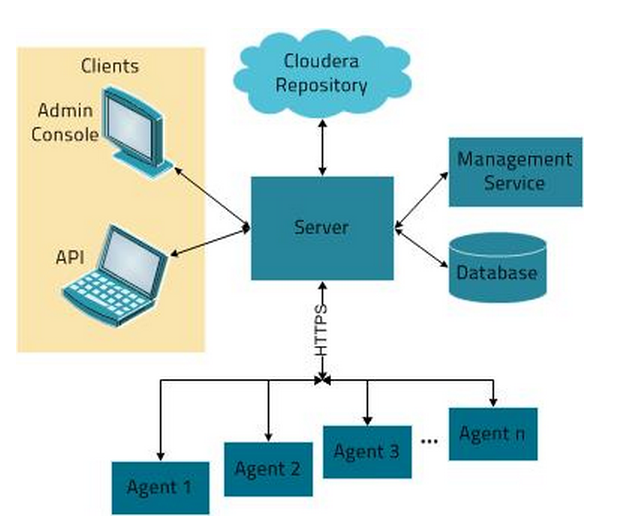
- Cloudera Manager Server
- Cloudera Management Service
- Relational databases (several)
- Filesystem-based runtime state storage (used by some services that are part of Cloudera Management Service)
- Cloudera Manager Agent (one instance per each managed host)
You can locate the Cloudera Manager Server and Cloudera Management Service on different hosts (with each role of the Cloudera Management Service, such as the Event Server or the Alert Server and so on, possibly located on different hosts).
Cloudera Manager Server and some of the Cloudera Management Service roles (such as Cloudera Navigator) use a relational database to store their operational data. Some other services (such as the Host Monitor and the Service Monitor) use the filesystem (through LevelDB) to store their data.
High availability in the context of Cloudera Manager involves configuring secondary failover instances for each of these services and also for the persistence components (the relational database and the file system) that support these services. For simplicity, this document assumes that all of the Cloudera Management Service roles are located on a single machine.
The Cloudera Manager Agent software includes an agent and a supervisor process. The agent process handles RPC communication with Cloudera Manager and with the roles of the Cloudera Management Service, and primarily handles configuration changes to your roles. The supervisor process handles the local Cloudera-deployed process lifecycle and handles auto-restarts (if configured) of failed processes.
| << Configuring Cloudera Manager for High Availability With a Load Balancer | ©2016 Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved | Prerequisites for Setting up Cloudera Manager High Availability >> |
| Terms and Conditions Privacy Policy |